Home > About us
Update:March 23, 2023
Main content starts here.
About us
Forest Tree Breeding Center (FTBC) is the largest institute of forest tree breeding in Japan.FTBC have 4 Regional Breeding Office.The main services are developing new varieties, collection and conservation/preservation of forest tree genetic resources and international technical cooperation.
・Developing new varieties
Superior varieties for growth and wood quality (fast growth, trunk straightness and mechanical strength.)Superior varieties for resistance against damages (Pine wilt nematode, snow pressure)Superior varieties for environmental and other services (pollen free or less pollen)
・Collection and conservation/preservation of forest tree genetic resources
Breeding materials for new varieties (Cedar, Cypress, etc.)
Endangered tree species and natural heritage trees (as a part of biodiversity national strategy)
・International technical cooperation
Developing breeding technique to adapt to climate change through international technical cooperation and collaborative research.
Development superior varieties for growth
FTBC selected about 9000 plus trees (Cedar, Cypress, Pine, etc.) which are superior for growth (wood volume).
To evaluate genetic ability of the plus trees, FTBC has planted 2,400 progeny test forests (3,200ha in total). FTBC has been conducting periodical (10 years, 20 years, 30 years old) monitoring of the progeny test forests.
As results of these progeny tests, FTBC developed 287 superior varieties for growth from
plus trees (first generation). FTBC conducted control crosses by use of superior first generation plus trees and grew population of subsequent generation. FTBC selected 757 second generation plus trees among the population by 2016.
 |
Excellent early growing F1 individual Age: 5 years Height 7 m (2.8m in 1st generation plus tree) Age: 10 years Height 12.8 m |
Development of pollen free and less pollen varieties
FTBC is leading in research and development of pollen free and less pollen varieties.
The allergy associated with tree pollen has been one of the social-medical issues in Japan. The number of Japanese cedar pollinosis is over 25 % of the population. FTBC is carrying to develop less pollen varieties, pollen less than 1 % of the ordinary tree, of Cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) and Japanese cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa) plus tree stock. Moreover, pollen free varieties of Cedar are also developed from stock of breeding materials in 2004 and 2007.
Hybrid trial between pollen free varieties and plus trees are being carried out for development new pollen free varieties with superior growth and wood quality.
FTBC developed 153 new cedar varieties (less pollen), 55 cypress varieties (less pollen), and 2 cedar varieties (pollen free or male sterile).
 |
 |
| Less pollen variety | Ordinary tree |
Tolerant varieties against pine wilt nematode
FTBC is leading in research and development of pine wilt nematode (Bursphelenchus xylophilus) tolerant varieties. In 1971, FFPRI researchers detected that nematode causes the pine wilt diseases.
Upon this result, FTBC started selection of pine wilt nematode tolerant varieties and succeeded in its development.
The pine wilt nematode damages are spreading to China, Korea, and Europe (Portugal and Spain).
FTBC has been carrying out research and development of pine wilt nematode tolerant varieties 429 new varieties are developed by 2016. As of 31 March 2017, 35 seed orchards of red pine (Pinus densiflora) and 46 seed orchards of black pine (Pinus thunbergii) have been established by resistant varieties.
 |
Pine wilt nematode (1mm length) Carried by Longhor beetle |
Outline of forest tree gene bank program
FTBC is the solo implementation agency for forest tree gene bank program in Japan. With taking due consideration to application value of genetic resources and/or needs and priority of conservation, FTBC is systematically conducting exploration and collection of genetic resources, and conserving/preserving such resources by seeds, pollen or propagated individuals. FTBC is also conducting trait evaluation of collected genetic resources for identification of potential use as well as distributing such resources for research purposes.
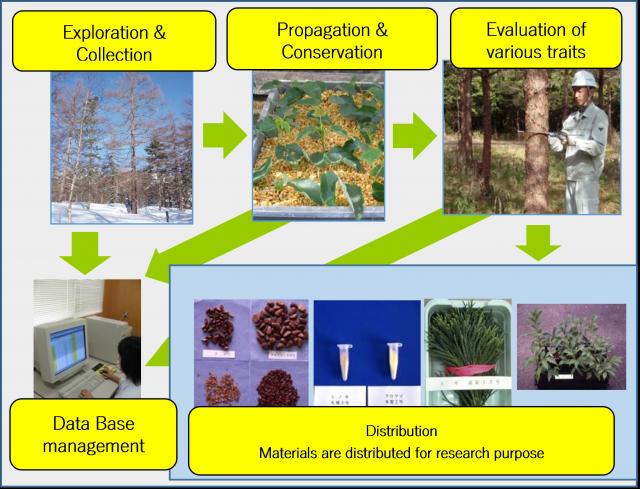 |
Clonal propagation services of natural heritage trees
Emergency call of natural heritage trees, bank services
Natural heritage trees and trees with long and distinguished history are the asset of local community or objects of faith as well as biological resources. Upon the request for clonal propagation of such trees, FTBC will propagate clonal successor saplings by cutting or grafting. These successor saplings will be returned to the original site while conserving in FTBC as research materials.
 |
Development of forest tree breeding techniques associated with international cooperation
Breeding of drought tolerant trees for adaptation to climate change in drylands of Kenya
Partner: Kenya Forestry Research Institute, Kyushu University, Japan International Cooperation Agency
Duration: 2012-2021
Species : Melia volkensii, Acacia tortilis
Purpose: To select and improve superior varieties of Melia volkensii and Acacia tortilis which have useful traits for plantation development in drylands of Kenya.
 |
 |
| Training in Japan | Dispatch of short term experts |
Breeding of Calophyllum inophyllum to contribute towards costal disaster prevention
Partner, Duration: Taiwan Forestry Research Institute, 2011-2021 Pacific Community, 2012-2022
Species: Calophyllum inophyllum
Purpose: To select superior trees which have useful traits to develop coastal disaster prevention forest.
 |
 |
| Calophyllum inophyllum | Test plantation in Taiwan |
Publications
Overview(FTBC,FBRC)(PDF:6,026KB)
Copyright © Forest Research and Management Organization. All rights reserved.
